Importance of Resolving Tax Debt for Passport Retention
Are you aware that unresolved tax debt can lead to the revocation or denial of your passport? According to U.S. regulations, the State Department has the authority to revoke or refuse to issue passports to individuals who owe federal tax debts of $59,000 or more, given a tax lien or levy has been filed against them.
It's essential to note that this regulation doesn't apply to individuals adhering to an installment agreement for their taxes, those declared bankrupt, residents of a federally declared disaster area, or people whose tax debts are deemed uncollectible due to hardship by the IRS.
The process for this involves the IRS providing the State Department with the names of taxpayers meeting these criteria. Those with certified debts are notified that their names have been submitted to the State Department, typically through a CP508C notice. Receiving this notice should prompt immediate contact with the IRS to arrange debt resolution.
The significance of this issue is emphasized by the rising number of legal cases involving passport revocations due to tax debts. In the U.S. Tax Court, the IRS has consistently emerged victorious in these cases.
For instance, in one case (Gayou, TC Memo. 2023-61), a man owing approximately $62,000 in tax debts across three years contended that his debt certification to the State Department by the IRS was erroneous. However, the Tax Court deemed the IRS's action appropriate and dismissed the case.
In another case (Meduty, 160 TC No. 13), a man with over $100,000 in tax debts spanning eight years claimed he never received the CP508C notice. The Tax Court ruled that an incorrect or missing notice doesn't invalidate the debt certification to the State Department.
These examples highlight the serious implications of outstanding tax debts on one's passport status, underlining the importance of addressing and resolving tax debts promptly.
Supreme Court Decision: IRS Can Summon Bank Records Without Third-Party Notifications
In the recent Polselli v. Internal Revenue Service case, the Supreme Court declared that the IRS is not required to notify third parties when summoning banking records in tax collection scenarios.
The case revolves around taxpayer Remo Polselli, who accumulated over $2 million in federal tax debt over several years. The IRS proceeded with collection efforts and obtained an order compelling Polselli to submit particular financial and business documents. Moreover, administrative summonses were served to banks where accounts were held by Polselli's wife, Hanna Karcho Polselli, and his legal counsel.
Such summonses typically demand specific information—in this case, financial records. The IRS' motive was to obtain information that might assist them in collecting the tax debt Polselli was already deemed to owe.
Notably, the IRS did not inform Polselli's wife or his lawyers about the summonses issued to the banks. It leaned on the exclusion clause in section 7609(c)(2)(D)(i) of the Tax Code, which allows for skipping notice in summonses issued "in aid of the collection" of tax assessments.
The case put a spotlight on whether the statutory exception to the notice requirement applies solely when a taxpayer has a legal interest in the accounts or records summoned by the IRS. In response, the Court concluded that "The notice exception does not contain such a limitation."
The statute (section 7609) lists three conditions under which the IRS can be exempted from giving notice:
- A summons must be "issued in aid of . . . collection."
- A summons must assist the collection of "an assessment made or judgment rendered."
- A summons must facilitate the collection of assessments or judgments "against the person with respect to whose liability the summons is issued."
The Court declared that none of the above components for dismissing notice in §7609(c)(2)(D)(i) require the taxpayer to hold a legal interest in the records sought by the IRS.
However, the Court clarified that its decision does not discount concerns about the broad scope of the IRS's authority to issue summonses. They acknowledged privacy considerations and emphasized that the IRS's authority to issue summonses "in aid of the collection" is not unlimited.
Despite this decision, the Supreme Court did not define the exact boundaries of the phrase "in aid of the collection." Nevertheless, the Court decisively answered the question at hand: the notice exception does not necessitate that a taxpayer maintain a legal interest in records summoned by the IRS. The answer, they concluded, is no.
Chief Justice Roberts delivered the unanimous opinion of the Court, and Justice Jackson filed a concurring opinion, joined by Justice Gorsuch.
For more information, please reach out to our office at (207) 901-1000 or www.proponotaxresolution.com.
The Ongoing Debate Over Maine's Income Tax Elimination Proposal

The contentious proposal to eliminate income tax in Maine has sparked significant discussion among residents, businesses, and lawmakers. The bill, which aims to phase out income tax over a five-year period starting in 2024, is currently facing staunch opposition from Democrats who control both the House and Senate in Maine's State House. Despite the uncertain future of the bill, its proponents argue that the bold move could lead to substantial financial benefits for Mainers, as well as businesses operating in the state.
Representative David Boyer of Poland has proposed the bill, which is designed to gradually reduce the state's tax each year. This approach allows each state department to make necessary adjustments to their annual budgets, providing ample time to identify wasteful spending and implement required cuts. Boyer contends that despite a 20% increase in the state's budget since the last budget, there has not been a corresponding improvement in services such as roads and other infrastructure projects.
However, opponents of the bill express concerns that the elimination of income tax would leave the state with insufficient funding to fulfill its responsibilities. This sentiment is echoed by House Speaker Mark Eves, a Democrat, who has stated that Maine's tax system is broken and disproportionately benefits those at the very top. Eves believes that the current proposal would only exacerbate the issue.
The concept of eliminating income tax in Maine is not new. In 2015, then-Governor Paul LePage proposed an amendment to the state's constitution to permanently prohibit the Legislature from imposing income tax on any person, starting in 2020. To compensate for lost revenues, LePage's two-year budget plan aimed to increase sales taxes, cut off state revenue sharing with local municipalities, and impose taxes on certain non-profit organizations.
LePage's proposal, however, met with fierce resistance from Democrats, who rejected the idea outright. In response, they offered a counter-proposal that called for a decrease, rather than elimination, of income tax, alongside lowered property taxes and an unchanged sales tax.
If the current bill is enacted and income from residents tax is abolished in Maine, the state would join the ranks of 10 other states that have either partially or completely eliminated their income tax. At present, seven states have no income tax, while New Hampshire and Tennessee tax only dividend and investment income.
Boyer concedes that the bill's passage in its current form is unlikely. Nevertheless, he remains dedicated to advocating for tax breaks wherever possible, in the hope of alleviating the financial burden on Maine's large retiree population, who live on fixed incomes, as well as benefiting higher-income "job creators."
The bill is anticipated to reach the House floor within the next 4-6 weeks, where its fate will be determined. In the meantime, the ongoing debate over the elimination of income tax in Maine continues to generate strong opinions from both supporters and detractors. Whether the bill ultimately succeeds or fails, the conversation surrounding Maine's tax system and potential reforms is not expected to dissipate anytime soon.
As Maine grapples with the prospect of income tax elimination, residents, businesses, and lawmakers must weigh the potential benefits against the concerns raised by its opponents. The outcome of this debate will have lasting implications for the state's financial landscape and may influence similar discussions in other states across the country. Regardless of the bill's eventual fate, the conversation it has sparked about Maine's tax system and the need for potential reforms highlights the importance of engaging in informed, balanced discussions around such critical issues.
Contact Propono for help with the IRS and the Maine Tax Authority.
IRS Unveils Detailed Strategy for Allocating $80 Billion in Additional Resources
In an extensive report submitted to the Secretary of the Treasury, the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) has presented its strategic operating plan for the upcoming decade. This plan details how the agency intends to utilize the extra $80 billion in funding it recently received to improve customer service, expand its ability to scrutinize large corporations and high-income individual taxpayers, and upgrade its obsolete systems and technology infrastructure.
Newly appointed IRS Commissioner Danny Werfel has expressed that the plan foresees a promising future for both taxpayers and the IRS. The agency will undergo a significant transformation in its operations, delivering the services that taxpayers are entitled to. Werfel also highlighted that the future IRS experience will be distinctly different from its current state, driven by substantial advancements in service and technology.
The IRS has developed the 150-page Strategic Operating Plan in response to the Inflation Reduction Act passed in August of the previous year, which allocated $80 billion in new funding to the agency over a ten-year period. The plan aims to address concerns about the use of these funds, as the initial announcement of the additional resources raised concerns that the IRS might target middle-class taxpayers and small businesses. This led Republicans in Congress to propose the withdrawal of the funding.
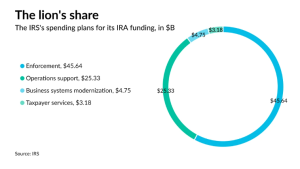
The IRS has specified that the $80 billion will be distributed across three primary areas:
- To "rebuild and strengthen" customer service operations, which experienced significant setbacks during the pandemic, resulting in infamously long wait times on IRS phone lines;
- To augment the agency's ability to audit high-income taxpayers (roughly 30,000 individuals earning more than $10 million per year) and intricate large businesses; and,
- To modernize the agency's numerous outdated technology systems.
The strategic plan includes 42 "key initiatives" and 190 "key projects" that the IRS will carry out over the next decade, with the option to introduce additional projects as required.
While the plan refers to the hiring of nearly 30,000 new employees, including 5,000 customer service representatives, it does not specify how many of these new hires will be assigned to enforcement roles. However, given that $45 billion of the total $80 billion is designated for enforcement, it is probable that a considerable number of new employees will be allocated to this area.
A significant portion of the new hires will offset ongoing attrition and the long-term reduction in funding and staffing levels. The IRS currently has around 80,000 employees, approximately 19% fewer than the 95,000 it had in 2010.
Werfel stressed that the agency has been unable to provide the level of service taxpayers deserve for several years. He stated that the IRS is enthusiastic about showcasing how the actions outlined in the plan will lead to concrete improvements for taxpayers, with technology and in-person assistance forming essential elements of this endeavor.
The commissioner asserted that the influence of the additional funding is already evident, as the first signs of change can be observed during this tax filing season. He referred to the substantial improvement in phone service due to increased staffing, the expansion of walk-in services nationwide, and the implementation of new digital tools as initial steps in this transformative process.
Top 10 Tips to Avoid Tax Auditing: Keep your finances in order with these expert suggestions

No one wants to face a tax audit, but the truth is that many taxpayers may unknowingly take actions that can raise red flags with the Internal Revenue Service (IRS). While there's no surefire way to completely avoid an audit, there are steps you can take to minimize the likelihood of drawing unwanted attention to your tax return. Here are our top 10 tips to help you avoid tax auditing and keep your finances in order.
Tax Tips: Be Accurate and Thorough
Accuracy is crucial when it comes to filing your taxes. Double-check your calculations, make sure you're using the correct tax forms, and ensure that you've provided complete and accurate information. This includes reporting all your income, as underreporting can trigger an audit. Don't forget to include even small amounts from side jobs, as the IRS will likely have a record of those earnings.
Report All 1099 and W-2 Income
The IRS receives copies of all your W-2 and 1099 forms, so it's essential to report all income received, including wages, interest, dividends, and freelance income. Double-check the amounts on your forms against what you report on your tax return to avoid discrepancies.
Avoid Filing Paper Returns
Filing your taxes electronically can significantly reduce the risk of making errors, as the software automatically checks for issues and prompts you to fix them. According to the IRS, the error rate for paper returns is around 21%, while the rate for electronically filed returns is only 0.5%.
Keep Organized Records
Maintaining well-organized and accurate records is essential to avoid discrepancies in your tax return. If you're audited, having clear documentation will make it easier to prove your deductions and credits. Keep receipts, invoices, and other financial records for at least three years, as this is the typical period the IRS can audit.
Be Cautious with Deductions
Claiming unusually high deductions can catch the attention of the IRS, especially if they're disproportionate to your income. While you should claim all legitimate deductions, be careful not to inflate your expenses. Always have documentation to back up your claims in case of an audit.
Be Mindful of Business Expenses
The IRS scrutinizes self-employed individuals and small business owners more closely than regular wage earners, as they have more opportunities to manipulate their income and expenses. Ensure you separate your personal and business expenses, and only claim deductions that are directly related to your business operations.
File on Time
Filing your tax return late or requesting multiple extensions can raise suspicion. To avoid drawing attention to your return, file on time and pay any taxes owed by the deadline.
Check Your Math
Simple mathematical errors are one of the most common reasons for the IRS to question a tax return. Double-check your calculations and consider using tax software to minimize the chance of errors.
Report Foreign Assets
If you have foreign bank accounts or assets, make sure to report them as required by law. Failing to disclose foreign financial assets can result in severe penalties and increase your likelihood of an audit.
Seek Professional Help
If you have a complicated tax situation, it's wise to consult with a tax professional who can help you navigate the process and ensure your return is accurate and compliant. They can also offer guidance on tax-saving strategies and help you avoid potential red flags.
While there's no foolproof way to avoid a tax audit, following these expert tax tips can help you minimize the risk and keep your finances in order. Remember, the key is to be accurate, thorough, and honest in your tax reporting. If you do find yourself facing an audit, you can contact Propono at (207) 901-1000 for a free consultation.
Form 1099-B can make it easy to report your cryptocurrency capital gains — but it may contain inaccurate or incomplete information about your tax liability.
In this guide, we’ll cover everything you need to know about Form 1099-B for cryptocurrency taxes. We’ll explain what you should do if you receive Form 1099-B and discuss why Form 1099-B can lead to tax reporting issues for crypto investors.
Do I have to report crypto on my taxes?
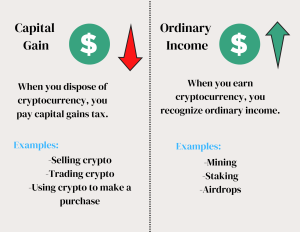
Cryptocurrency is considered property by the IRS and is subject to capital gains and ordinary income tax.
What is Form 1099-B?
Form 1099-B is a tax form designed to track the disposals of capital assets. The form contains details about cost basis, gross proceeds, and capital gains and losses.
Like other 1099 forms, Form 1099-B is issued to taxpayers and to the IRS.
Stockbrokers like Robinhood and eTrade typically send out 1099-Bs for your stock trading activity at the end of the year. At this time, cryptocurrency exchanges are not required to send 1099-Bs to customers.
Do you get a 1099-B for cryptocurrency?
As of 2021, there hasn’t been explicit guidance around what 1099s cryptocurrency exchanges should provide to customers and the IRS. As a result, different exchanges take different approaches to tax reporting.
While some exchanges issue 1099-B to customers, most currently do not send tax forms detailing capital gains and losses to customers.
This will change in the near future. The Build Back Better Act included requirements for cryptocurrency brokers to report capital gains and losses to customers and the IRS.
 It’s not yet clear when mandatory 1099 reporting will go into effect. The IRS announced in December 2022 that these requirements would be delayed indefinitely.
It’s not yet clear when mandatory 1099 reporting will go into effect. The IRS announced in December 2022 that these requirements would be delayed indefinitely.
What tax forms should I receive from cryptocurrency exchanges?
Cryptocurrency exchanges may send you other versions of Form 1099 — such as Form 1099-MISC and Form 1099-K.
Does Coinbase issue Form 1099-B?
Like other major exchanges, Coinbase currently does not issue Form 1099-B to customers and the IRS. For more information, check out our guide: Does Coinbase Report to the IRS?
Which exchanges issue 1099-B?
Here are some popular exchanges that issued Form 1099-B to customers for the 2021 tax year.
Bittrex
BlockFi
Cash App
Robinhood
Uphold
Do I need to include 1099-B on my tax return?
There’s no need to attach Form 1099-B on your tax return, but you can use the information on the form to keep track of your capital gains and losses.
What happens if I don’t report 1099-B income to the IRS?
If you don’t report taxable income that’s been reported to the IRS on Form 1099-B, it’s likely that your tax return will be flagged automatically and you will be sent a warning letter about your unpaid tax liability.
Remember, all of your cryptocurrency disposals and income are required to be reported whether they are on Form 1099 or not. The IRS can often track your cryptocurrency transactions even if they are not mentioned on these tax forms.
How do I report cryptocurrency disposals?
All cryptocurrency disposals (including those reported on a 1099-B) should be reported on Form 8949, along with a description of the property, your cost basis and gross proceeds, and the date you acquired and disposed of your assets.
For more information, check out our guide to reporting your cryptocurrency taxes.
What happens if I didn’t get a 1099-B from my exchange?
You are required to report all your taxable transactions to the IRS regardless of whether your exchange sends relevant tax forms. Failure to do so is considered tax fraud.
Which crypto exchanges do not report to the IRS?
At this time, centralized exchanges like KuCoin and decentralized exchanges like Uniswap do not issue Form 1099-B or other tax forms to the IRS.
Still, it’s important to remember that not reporting your cryptocurrency income on your tax return can lead to fines, audits, and even potential jail time.
For more information, check out our guide to non-KYC exchanges.
Why does my Form 1099-B have incomplete/inaccurate information?
Transfers between different exchanges and wallets can lead to inaccuracies on Form 1099-B. In these situations, your cryptocurrency exchange might not have data on cost basis that’s needed to calculate your capital gains and losses.
For example, consider the following scenario.
This guide covers everything you need to know about Form 1099-B for cryptocurrency taxes, including why it can lead to tax reporting issues for crypto investors. Although Form 1099-B can simplify reporting your cryptocurrency capital gains, it may contain incomplete or inaccurate information about your tax liability.
If you're wondering whether you need to report cryptocurrency on your taxes, the answer is yes. The IRS considers cryptocurrency property and subject to capital gains and ordinary income tax.
Form 1099-B is a tax form specifically designed to track the disposals of capital assets, including cryptocurrency. The form contains important information such as cost basis, gross proceeds, and capital gains and losses. Like other 1099 forms, it's issued to both taxpayers and the IRS.
While stockbrokers like Robinhood and eTrade typically send out 1099-Bs for your stock trading activity at the end of the year, cryptocurrency exchanges are not currently required to send 1099-Bs to customers. However, some exchanges may send other versions of Form 1099, such as Form 1099-MISC or Form 1099-K.
It's important to note that failure to report taxable income, whether it's been reported on a 1099-B or not, can lead to fines, audits, and even potential jail time. Even if your exchange doesn't issue a 1099-B, you're still required to report all your taxable transactions to the IRS.
If you do receive a 1099-B from your exchange, you don't need to attach it to your tax return, but you can use the information on the form to keep track of your capital gains and losses. You should report all cryptocurrency disposals, including those reported on a 1099-B, on Form 8949, along with a description of the property, your cost basis and gross proceeds, and the date you acquired and disposed of your assets.
It's worth noting that different exchanges take different approaches to tax reporting, and as of 2021, there hasn't been explicit guidance around what 1099s cryptocurrency exchanges should provide to customers and the IRS. While some exchanges issue 1099-Bs to customers, most currently do not send tax forms detailing capital gains and losses to customers. However, the Build Back Better Act included requirements for cryptocurrency brokers to report capital gains and losses to customers and the IRS, although it's not yet clear when mandatory 1099 reporting will go into effect.
How to Prepare for an IRS Audit
Filing taxes can be a daunting process, but for some it's much more than that - an IRS tax audit. This stressful situation involves having the IRS put your tax return under a microscope to see if you reported all your income and to see if you overstated your deductions and expenses. The IRS’s main goal in an audit is to assess more tax, penalties and interest. It’s an intimidating experience that most Americans dread facing!
An IRS audit can cause even the most squeaky-clean of taxpayers to become fearful and anxious when faced with defending yourself to an auditor. It's understandable why the majority feel powerless in this situation. You also have to understand, and get comfortable with, in the eyes of an IRS auditor, you are guilty until proven innocent. Navigating the tax code on your own is not a good place to be.
Tax audits don't have to be a source of fear as long as you've remained compliant with all the rules and regulations. The best way to ensure peace of mind is to work with an experienced Tax Resolution Specialist who represents clients in such matters and has a good track record. Contact our firm for a complimentary no obligation consultation to assess your situation. HeritageTaxCompany.com
An IRS audit can be a very time consuming and intrusive exercise that can include a visit from the auditor. Audits can also be conducted remotely. This method, known as a desk audit, involves sending documents through fax or mail to evaluate accuracy and compliance with established law.
Filing taxes is a complex process and the IRS seeks to ensure accuracy by auditing income tax returns. These examinations may be focused on certain deductions, particularly if taxpayers have claimed for more than what their reported incomes suggest - but this does not necessarily indicate any wrong-doing or misconduct. The IRS can also select your return to be audited for no reason at all. These are referrer to as “random” audits to ensure compliance with the tax laws.
Taxes are a fundamental pillar of our society and the government strives to ensure that everyone is compliant. To this end, random audits from both Federal and State authorities may be conducted in order to verify taxpayers' income as well as expenses incurred throughout the year; making sure all taxation payments due remain accurate.
Preparing for an IRS tax audit should be an ongoing process. To avoid any problems, ensure that all deductions taken are backed up with proof and every receipt is kept on file along with the return - you never know what may arise in the future! It's important to remember: only declare items which can easily be defended - your documents are a crucial piece to your defense. Ensure each tax record remains safely stored away for at least seven years as per IRS regulations.
Protect your finances and future by taking the time to review your tax returns before signing off, even if you have a professional do them. A thorough examination of the documents will not only help ensure accuracy in filing but also offers an invaluable opportunity for you to gain knowledge on taxes - safeguarding against potential penalties or interest charges related to inaccuracies down the line.
Tax audits can be intimidating, but with a little foresight and the right representation it doesn't have to cause stress. Staying organized throughout the year is key for having peace of mind when tax season rolls around. Finding an experienced professional who understands your individual needs will help make dealing with the audit as painless as possible.
Take the worry out of representing yourself in front of the IRS, which is like going to court without a lawyer. Let our expert team lift this from your shoulders and navigate the IRS on your behalf. Schedule a no-obligation consultation to explore your options and get on track towards permanently resolving any worries you have over having to meet with and defend yourself in an IRS or State income tax audit.
How to Avoid an Expensive Tax Bill…What to Do If You Receive One
Tax bill season can be a time of great anticipation for millions of Americans with dreams of a nice, big, refund check coming soon. Yet this year, many Americans may find themselves surprised and coming up short on their refunds.
Many taxpayers have been shocked to find that this year, instead of a big tax refund check arriving in the mail, they are being saddled with an unexpected bill from Uncle Sam. The combination of recent tax law changes and updated employer withholding tables has left individuals scrambling to figure out how to pay for their new IRS obligations due at filing time.
If you're worried about a looming tax bill, never fear: there are measures you can take to ensure that your taxes don't unexpectedly balloon. From budgeting tips to what do when the worst happens, these strategies will have your wallet breathing easy throughout the year!
The Earlier the Better!
Ignoring an IRS debt could ultimately result in serious consequences. It is in your best interest to be aware of any outstanding amount as soon as possible, providing time for tax planning and sourcing the necessary funds.
Don't let late payments rack up and cause costly penalties and interest. Be proactive about filing your taxes so you'll have a good idea of what will be owed, if anything, that is needed to be paid on time.
Pay Attention to Your Paychecks
With the recent changes in tax law, your paychecks may have grown more generous - but don't get too excited! They could mean less of a refund or an unexpected bill when you file. Make sure to stay informed and plan ahead so unpleasant surprises won't come back to haunt you this filing season.
To prepare for tax season, it's important to monitor your paychecks and ensure that the right amount is withheld. If you see a decrease in federal taxes being taken out of each paycheck, adjust this with your employer immediately - even though it may mean taking home less every month. Doing so can help protect you from federal and state tax debts and penalties later!
Run Your Numbers Before
With just your final paycheck from last year and a few additional details, you can gain insight into what kind of tax refund or balance due to expect come filing season. It pays to take the time for preparation now so there are no unpleasant surprises later! However, please note that you should never use your 2022 final paycheck to prepare your return. You’ll need the actual W-2 from your employer in order to file a complete and accurate return.
To be prepared for tax season, compile all necessary records of your income, credits and deductions to estimate what you owe. Leverage the power of a reliable tax preparation software or use an everyday calculator with those numbers in hand to better understand your financial situation.
Know You Have Back Taxes or Will Owe A Lot?
Ignoring a tax bill isn't an option; the IRS will always come knocking. Settling it quickly can save you from further financial trouble, so don't delay. Your taxes may burden your wallet now, but they'll take hefty chunks out of your future if left unresolved!
Dealing with the IRS can be a daunting experience for many taxpayers. Even getting the IRS on the phone these days is nearly impossible. Without proper guidance, and expert help, attempting to negotiate your own tax problem is like going to court without a lawyer - not a wise move!
Struggling with tax burdens from the IRS or State? Our experienced team knows the IRS’s “ins and outs”, knows how to navigate the IRS maze and is here to assist you in finding a resolution that works best for your unique situation. Take advantage of our knowledge and expertise by booking an appointment with us today - take control of your taxes, and your life, before they become unmanageable! 


What is a Federal Tax Lien Notice & What Should You Do If You Receive One?
Ignoring your obligation to pay taxes can lead the federal government to conduct severe legal action against all of your existing assets, current and future income and assets you acquire in the future; this form of punishment is called a federal tax lien.
If you've received a certified letter indicating that the federal government has placed an unwelcome Federal 'tax lien' on your assets, this article can provide insights into what it means and how to remedy the issue.
 What is a Federal Tax Lien?
What is a Federal Tax Lien?
When a taxpayer falls behind on their federal taxes, they are at risk of having an official public notification filed against them. This document is known as a Notice of Federal Tax Lien and can cause serious consequences for the individual's ability to enjoy any financial security.
A federal tax lien is an official document filed with the county recorder’s office (usually where the taxpayer lives or conducts business) and the secretary of state's office (if it’s a corporation or partnership) notifying the general public that a taxpayer has an unpaid federal tax debt.
Lien vs. Levy
For the unaware taxpayer, it is important to understand the difference between liens and levies. People will use them interchangeably, but they are very different. A lien grants the government legal rights over all of your property. This does not mean they are going to sell your property but it does make it difficult for you when the government has an ownership stake in your assets. Especially if you are looking to sell them, like real estate. Anything you sell, the IRS will receive its cut before you receive anything.
A levy, on the other hand, is the physical seizure of income and assets. The IRS is the only creditor on the planet that can garnish your income and remove money from your bank account without a court order.
This may affect your credit.
The consequences of an IRS filing a Notice of Federal Tax Lien are significant. This lien is public record, and eventually may show up on one's credit report which can severely impact their ability to secure further credit in the future as well as lower their credit score.
The effects on your assets.
A federal tax lien restricts your ability to utilize and monetize any existing or future assets - from real-estate, stock investments, automobiles, etc. This means that the IRS is first in line for proceeds if you were to sell any of your assets, before you receive any cash.
The affects on your business.
Protecting your business from financial troubles is important, and a lien can be especially damaging. It attaches to all of your property — including accounts receivable –which could seriously impact the normal day to day operations of your business, leaving you further in debt than before.
Thinking about filing for bankruptcy?
Although filing for bankruptcy may offer relief from debt, it's important to note that your tax obligations and Notice of Federal Tax Lien still remain in effect. To ensure financial freedom, take steps to address any existing unpaid taxes before planning a successful future.
When a levy is enforced, it can result in the government seizing funds from your bank account or drastically reducing up to 75% of your net pay.
Next Steps
Paying off your tax debt in full is the most effective way to erase a federal lien. Typically the IRS will release the lien within one month of payment. But if you are unable to pay such a large sum, as most people are, at once don't lose hope - this is where a tax resolution specialist can help.
When it comes to the IRS, navigating legal channels on one's own is a risky endeavor. The best course of action for those facing tax issues is to seek out expert, professional help by calling an experienced and qualified tax resolution provider like us. With our expertise right by your side, your chances of achieving a positive outcome improve significantly!
Reach out to our firm and we’ll schedule a no-obligation confidential consultation to explain your options to permanently resolve your tax problem once and for all.
Do You Owe Money to the IRS but Can't Pay? Try This.
When you owe back taxes and can’t afford to make any payments, then it may be time for a special tax status known as currently not collectible. This means that your debt is still considered valid even though there's no chance at recovery right now. When you’re approved for currently not collectible status, the IRS can no longer garnish your wages or seize any property.
Now, don't forget about these debts because the IRS is still looking for payment.
What is Currently Not Collectible Status?
The IRS will place your account in currently not collectible status if you can’t pay both back taxes and reasonable living expenses. You may request this by submitting the proper form with documentation that proves how much income you have left over that is available to make a payment, along with any assets that have been sold recently to cover mounting debts - like homes!
To qualify for the currently not collectible status, you will need to put together a case that you will present to the IRS. Gather copies of your bills, proof of your income (pay stubs, bank statements, alimony, etc), and your investments. It is important to document your inability to pay so that if the IRS determines you cannot afford your necessary expenses, it can grant you status.
When dealing with the IRS, it is best to have a professional in your corner. The IRS can be very intimidating and might ask invasive questions that could land you deeper into trouble than before if you do not know how to answer properly. Remember - they are not friends of yours; their job entails collecting what they believe you owe them so make sure any interaction stays as simple and effective as possible. That is why it is crucial to reach out for help from one our tax resolution specialists.
Temporary Solution
If your status is approved, it does not mean you do not have to file your current and future taxes. This status only applies to your back taxes that the IRS is looking to collect. The currently not collectible status is simply a bandaid to help you get back on your feet. That way you can put yourself in a better position to make a payment in the future. The IRS may review your status every year or two if it looks like there is potential for repayment. You will only be able to keep the status active if you still can not make a payment on your back taxes.
Statute of Limitations
The IRS is an institution that prides itself on being collections-oriented. They will try to collect outstanding taxes for only 10 years from the date they were assessed against you. Once the 10 years is up, the IRS can no longer collect the back taxes. This also applies if you have the currently not collectible status. If you do not have the status, or are in an installment agreement, or have an offer in compromise pending, the IRS can garnish wages and add more penalties to your case making things worse for you as well as your wallet.
In today's tough economic climate, many families are struggling to make ends meet. If you're worried about the IRS garnishing your wages or levying bank accounts, or filing liens against your property for non-payment of taxes you owe - then reaching out may give you some peace of mind.
Our firm will help explain all options available in order to relieve any anxiety associated with these situations because we know how intimidating this can be if nothing has been done before. There is a solution to every IRS problem. Connect with one of our tax resolution specialists to see if you qualify for the currently not collectible status, or any of the other IRS settlement options you may be eligible for and the best next steps for your situation.
Propono Tax Re : Soulution
207-901-1000
925 Main Street
Waterboro, Maine 04087